👤 UC Mode
 UC Mode 👤
UC Mode 👤
👤 SeleniumBase UC Mode (Undetected-Chromedriver Mode) allows bots to appear human, which lets them evade detection from anti-bot services that try to block them or trigger CAPTCHAs on various websites.
(For the successor to plain UC Mode, see CDP Mode 🐙)¶
(Watch the 1st UC Mode tutorial on YouTube! ▶️)
(Watch the 2nd UC Mode tutorial on YouTube! ▶️)
(Watch the 3rd UC Mode tutorial on YouTube! ▶️)
(Watch the 4th UC Mode tutorial on YouTube! ▶️)
👤 UC Mode is based on undetected-chromedriver. UC Mode includes multiple updates, fixes, and improvements, such as having special uc_*() methods for bypassing CAPTCHAs.
👤 Here's a simple example with the Driver manager:
from seleniumbase import Driver
driver = Driver(uc=True)
url = "https://gitlab.com/users/sign_in"
driver.uc_open_with_reconnect(url, 4)
driver.uc_gui_click_captcha()
driver.quit()
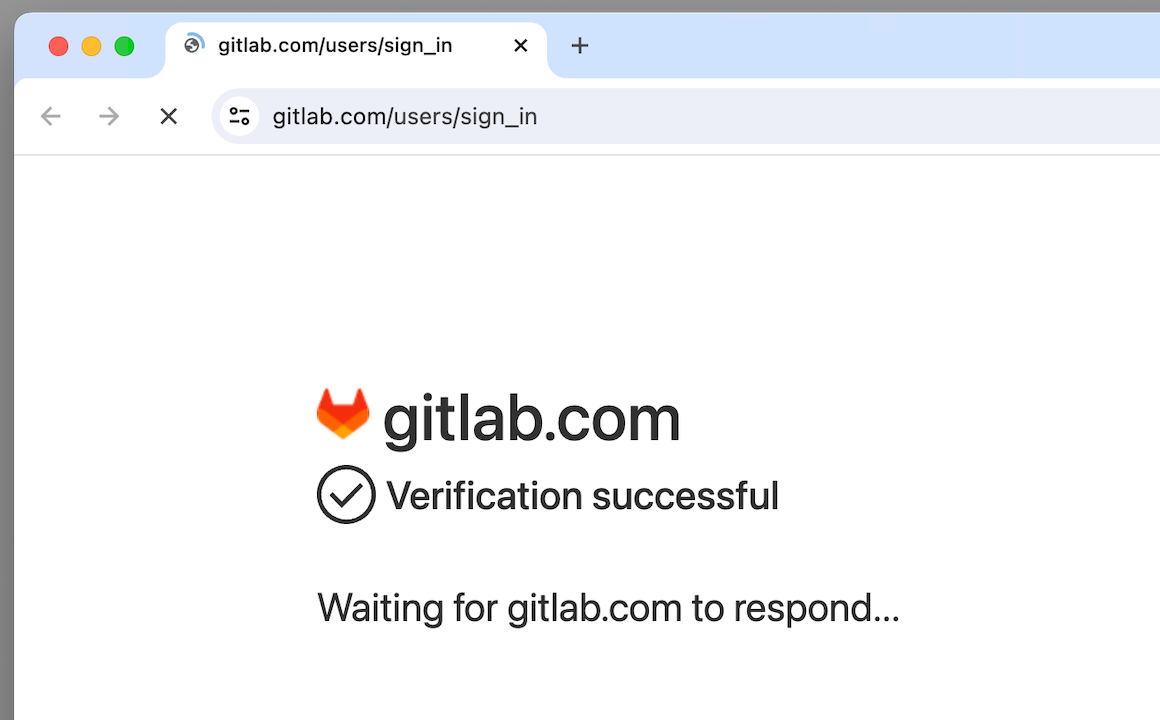
👤 Here's an example with the SB manager (which has more methods and functionality than the Driver format):
from seleniumbase import SB
with SB(uc=True) as sb:
url = "https://gitlab.com/users/sign_in"
sb.uc_open_with_reconnect(url, 4)
sb.uc_gui_click_captcha()
(Note: If running UC Mode scripts on headless Linux machines, then you'll need to use the SB manager instead of the Driver manager because the SB manager includes a special virtual display that allows for PyAutoGUI actions.)
👤 Here's a longer example: (Note that sb.uc_gui_click_captcha() performs a special click using PyAutoGUI if a CAPTCHA is detected.)
from seleniumbase import SB
with SB(uc=True, test=True) as sb:
url = "https://gitlab.com/users/sign_in"
sb.uc_open_with_reconnect(url, 4)
sb.uc_gui_click_captcha()
sb.assert_text("Username", '[for="user_login"]', timeout=3)
sb.assert_element('label[for="user_login"]')
sb.highlight('button:contains("Sign in")')
sb.highlight('h1:contains("GitLab")')
sb.post_message("SeleniumBase wasn't detected", duration=4)
👤 Here's an example where clicking the checkbox is required, even for humans:
(Commonly seen on forms that are CAPTCHA-protected.)
from seleniumbase import SB
with SB(uc=True, test=True) as sb:
url = "https://seleniumbase.io/apps/turnstile"
sb.uc_open_with_reconnect(url, reconnect_time=2)
sb.uc_gui_handle_captcha()
sb.assert_element("img#captcha-success", timeout=3)
sb.set_messenger_theme(location="top_left")
sb.post_message("SeleniumBase wasn't detected", duration=3)
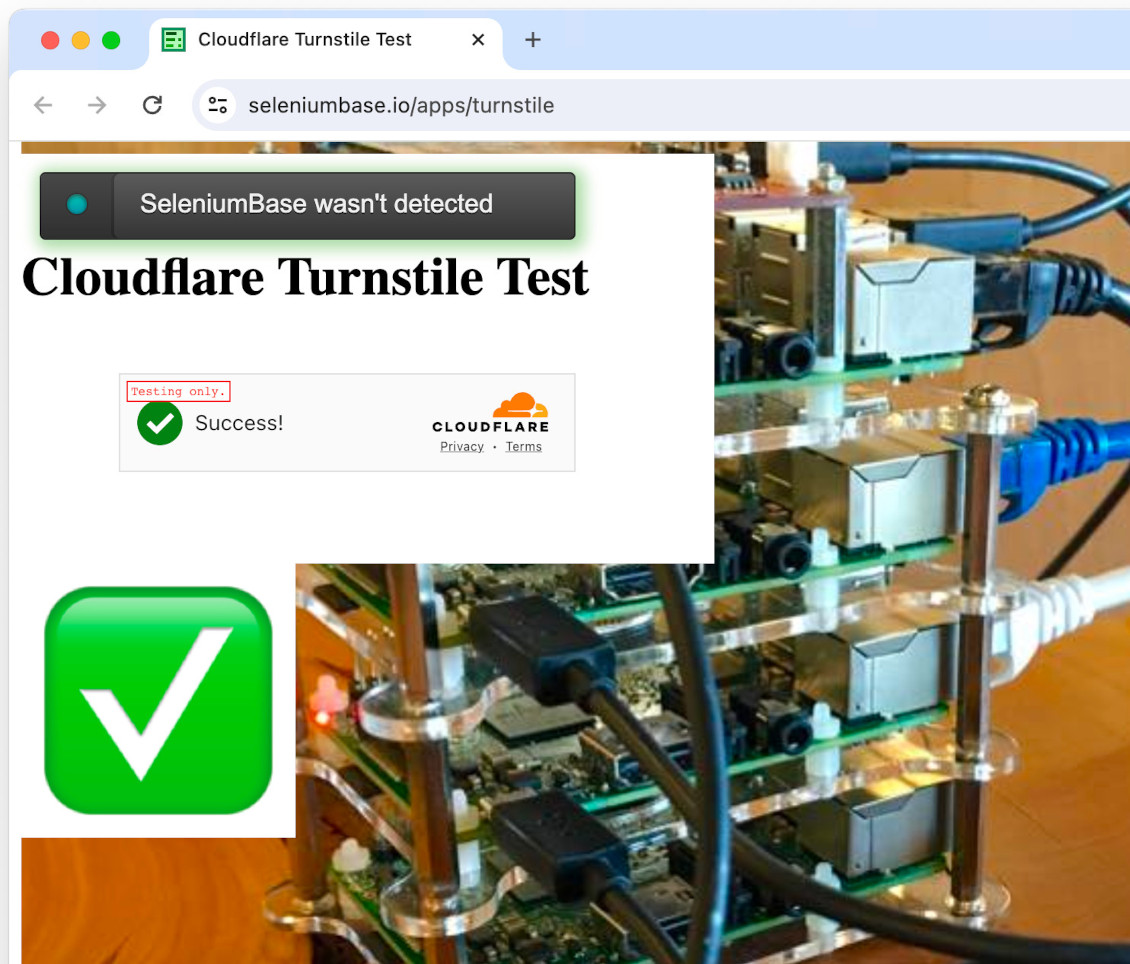
If running on a Linux server, uc_gui_handle_captcha() might not be good enough. Switch to uc_gui_click_captcha() to be more stealthy. Note that these methods auto-detect between CF Turnstile and Google reCAPTCHA.
Sometimes you need to add incognito=True with uc=True to maximize your anti-detection abilities. (Some websites can detect you if you don't do that.)
👤 Here's an example where the CAPTCHA appears after submitting a form:
from seleniumbase import SB
with SB(uc=True, test=True, incognito=True, locale="en") as sb:
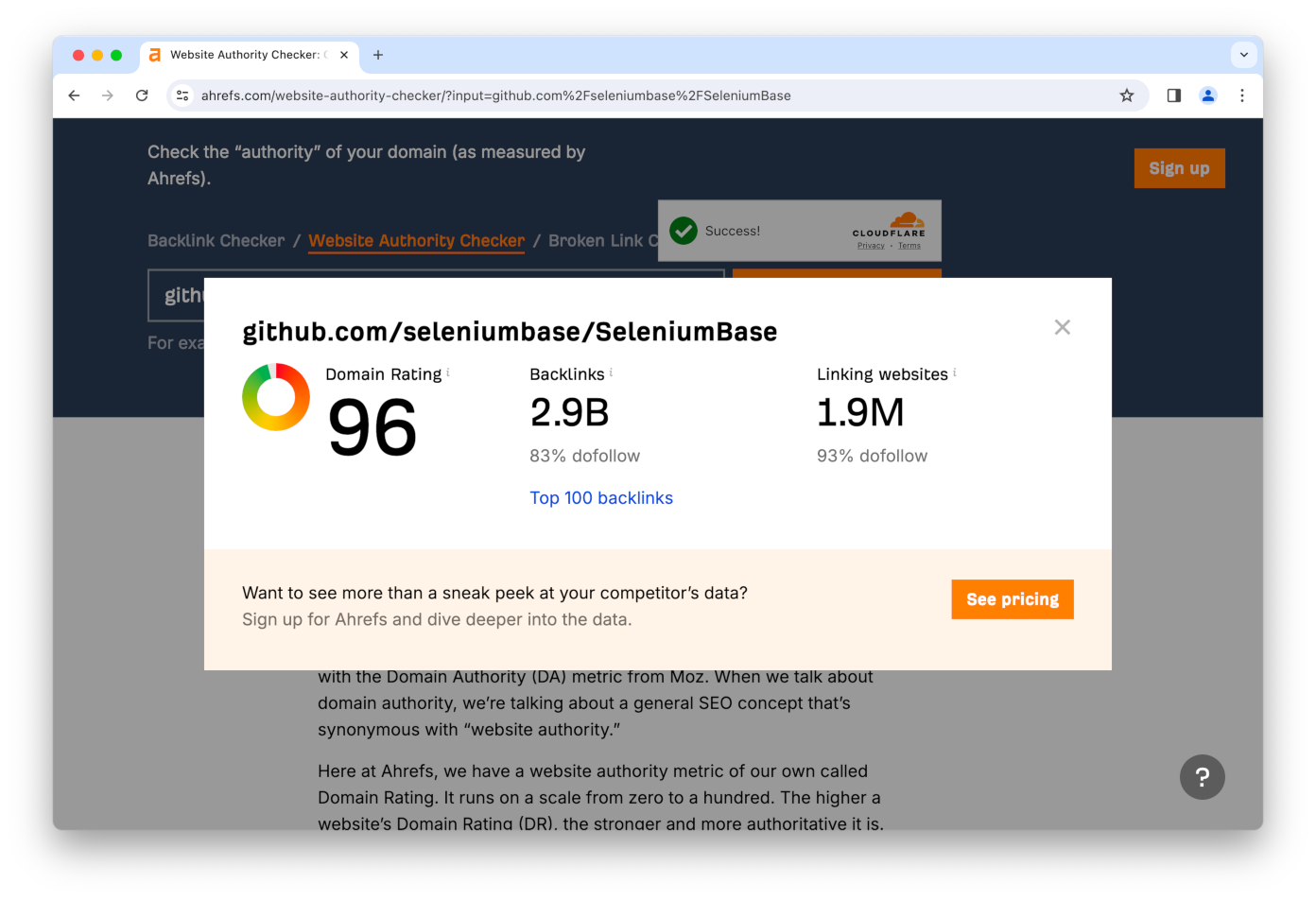
url = "https://ahrefs.com/website-authority-checker"
input_field = 'input[placeholder="Enter domain"]'
submit_button = 'span:contains("Check Authority")'
sb.uc_open_with_reconnect(url) # The bot-check is later
sb.type(input_field, "github.com/seleniumbase/SeleniumBase")
sb.uc_click(submit_button, reconnect_time=3.25)
sb.uc_gui_click_captcha()
sb.wait_for_text_not_visible("Checking", timeout=15)
sb.click_if_visible('button[data-cky-tag="close-button"]')
sb.highlight('p:contains("github.com/seleniumbase/SeleniumBase")')
sb.highlight('a:contains("Top 100 backlinks")')
sb.set_messenger_theme(location="bottom_center")
sb.post_message("SeleniumBase wasn't detected!")
👤 On Linux, use sb.uc_gui_click_captcha() to handle CAPTCHAs (Cloudflare Turnstiles):
from seleniumbase import SB
with SB(uc=True, test=True) as sb:
url = "https://www.virtualmanager.com/en/login"
sb.uc_open_with_reconnect(url, 4)
print(sb.get_page_title())
sb.uc_gui_click_captcha() # Only used if needed
print(sb.get_page_title())
sb.assert_element('input[name*="email"]')
sb.assert_element('input[name*="login"]')
sb.set_messenger_theme(location="bottom_center")
sb.post_message("SeleniumBase wasn't detected!")
The 2nd print() should output Virtual Manager, which means that the automation successfully passed the Turnstile.
(Note: UC Mode is detectable in Headless Mode, so don't combine those options. Instead, use xvfb=True / --xvfbon Linux for the special virtual display, which is enabled by default when not changing headed/headless settings.)
👤 In UC Mode, driver.get(url) has been modified from its original version: If anti-bot services are detected from a requests.get(url) call that's made before navigating to the website, then driver.uc_open_with_reconnect(url) will be used instead. To open a URL normally in UC Mode, use driver.default_get(url).
👤 Here are some examples that use UC Mode¶
- SeleniumBase/examples/verify_undetected.py
- SeleniumBase/examples/raw_turnstile.py
- SeleniumBase/examples/raw_form_turnstile.py
- SeleniumBase/examples/raw_uc_mode.py
👤 Here's an example where incognito=True is needed for bypassing detection:
from seleniumbase import SB
with SB(uc=True, incognito=True, test=True) as sb:
sb.driver.uc_open_with_reconnect("https://pixelscan.net/", 10)
sb.sleep(2)
![]()
👤 Here are the SeleniumBase UC Mode methods: (--uc / uc=True)¶
driver.uc_open(url)
driver.uc_open_with_tab(url)
driver.uc_open_with_reconnect(url, reconnect_time=None)
driver.uc_open_with_disconnect(url, timeout=None)
driver.reconnect(timeout)
driver.disconnect()
driver.connect()
driver.uc_click(
selector, by="css selector",
timeout=settings.SMALL_TIMEOUT, reconnect_time=None)
driver.uc_gui_press_key(key)
driver.uc_gui_press_keys(keys)
driver.uc_gui_write(text)
driver.uc_gui_click_x_y(x, y, timeframe=0.25)
driver.uc_gui_click_captcha(frame="iframe", retry=False, blind=False)
# driver.uc_gui_click_cf(frame="iframe", retry=False, blind=False)
# driver.uc_gui_click_rc(frame="iframe", retry=False, blind=False)
driver.uc_gui_handle_captcha(frame="iframe")
# driver.uc_gui_handle_cf(frame="iframe")
# driver.uc_gui_handle_rc(frame="iframe")
(Note that the reconnect_time is used to specify how long the driver should be disconnected from Chrome to prevent detection before reconnecting again.)
👤 Since driver.get(url) is slower in UC Mode for bypassing detection, use driver.default_get(url) for a standard page load instead:
driver.default_get(url) # Faster, but Selenium can be detected
👤 Here are some examples of using those special UC Mode methods: (Use self.driver for BaseCase formats. Use sb.driver for SB() formats):
url = "https://gitlab.com/users/sign_in"
driver.uc_open_with_reconnect(url, reconnect_time=3)
driver.uc_open_with_reconnect(url, 3)
driver.reconnect(5)
driver.reconnect(timeout=5)
👤 You can also set the reconnect_time / timeout to "breakpoint" as a valid option. This allows the user to perform manual actions (until typing c and pressing ENTER to continue from the breakpoint):
url = "https://gitlab.com/users/sign_in"
driver.uc_open_with_reconnect(url, reconnect_time="breakpoint")
driver.uc_open_with_reconnect(url, "breakpoint")
driver.reconnect(timeout="breakpoint")
driver.reconnect("breakpoint")
(Note that while the special UC Mode breakpoint is active, you can't use Selenium commands in the browser, and the browser can't detect Selenium.)
👤 On Linux, use xvfb=True / --xvfb to activate a special virtual display. This allows you to run a regular browser in an environment that has no GUI. This is important for two reasons: One: UC Mode is detectable in headless mode. Two: pyautogui doesn't work in headless mode. (Note that some methods such as uc_gui_click_captcha() require pyautogui for performing special actions.)
👤 uc_gui_click_captcha() auto-detects the CAPTCHA type before trying to click it. This is a generic method for both CF Turnstile and Google reCAPTCHA. It will use the code from uc_gui_click_cf() and uc_gui_click_rc() as needed.
👤 uc_gui_click_cf(frame="iframe", retry=False, blind=False) has three args. (All optional). The first one, frame, lets you specify the selector above the iframe in case the CAPTCHA is not located in the first iframe on the page. (In the case of Shadow-DOM, specify the selector of an element that's above the Shadow-DOM.) The second one, retry, lets you retry the click after reloading the page if the first one didn't work (and a CAPTCHA is still present after the page reload). The third arg, blind, (if True), will retry after a page reload (if the first click failed) by clicking at the last known coordinates of the CAPTCHA checkbox without confirming first with Selenium that a CAPTCHA is still on the page.
👤 uc_gui_click_rc(frame="iframe", retry=False, blind=False) is for reCAPTCHA. This may only work a few times before not working anymore... not because Selenium was detected, but because reCAPTCHA uses advanced AI to detect unusual activity, unlike the CF Turnstile, which only uses basic detection.
👤 To find out if UC Mode will work at all on a specific site (before adjusting for timing), load your site with the following script:
from seleniumbase import SB
with SB(uc=True) as sb:
sb.uc_open_with_reconnect(URL, reconnect_time="breakpoint")
(If you remain undetected while loading the page and performing manual actions, then you know you can create a working script once you swap the breakpoint with a time and add special methods like sb.uc_click as needed.)
👤 Multithreaded UC Mode:
If you're using pytest for multithreaded UC Mode (which requires using one of the pytest syntax formats), then all you have to do is set the number of threads when your script runs. (-n NUM) Eg:
pytest --uc -n 4
(Then pytest-xdist is automatically used to spin up and process the threads.)
If you don't want to use pytest for multithreading, then you'll need to do a little more work. That involves using a different multithreading library, (eg. concurrent.futures), and making sure that thread-locking is done correctly for processes that share resources. To handle that thread-locking, include sys.argv.append("-n") in your SeleniumBase file.
Here's a sample script that uses concurrent.futures for spinning up multiple processes:
import sys
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
from seleniumbase import Driver
sys.argv.append("-n") # Tell SeleniumBase to do thread-locking as needed
def launch_driver(url):
driver = Driver(uc=True)
try:
driver.get(url=url)
driver.sleep(2)
finally:
driver.quit()
urls = ['https://seleniumbase.io/demo_page' for i in range(3)]
with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=len(urls)) as executor:
for url in urls:
executor.submit(launch_driver, url)
👤 What makes UC Mode work?
Here are the 3 primary things that UC Mode does to make bots appear human:
- Modifies
chromedriverto rename Chrome DevTools Console variables. - Launches Chrome browsers before attaching
chromedriverto them. - Disconnects
chromedriverfrom Chrome during stealthy actions.
For example, if the Chrome DevTools Console variables aren't renamed, you can expect to find them easily when using selenium for browser automation:
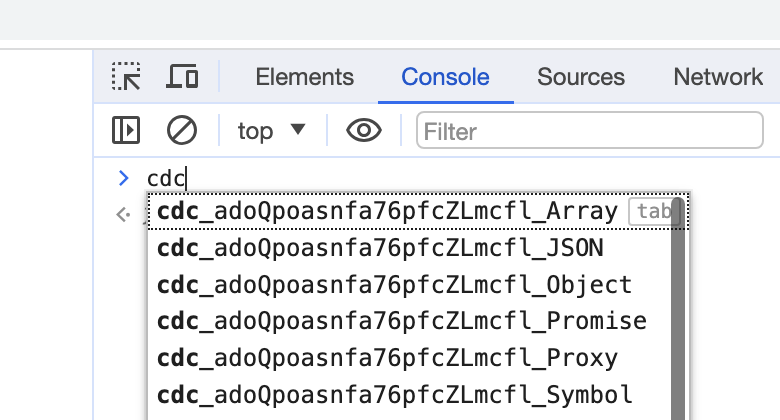
(If those variables are still there, then websites can easily detect your bots.)
If you launch Chrome using chromedriver, then there will be settings that make your browser look like a bot. (Instead, UC Mode connects chromedriver to Chrome after the browser is launched, which makes Chrome look like a normal, human-controlled web browser.)
While chromedriver is connected to Chrome, website services can detect it. Thankfully, raw selenium already includes driver.service.stop() for stopping the chromedriver service, driver.service.start() for starting the chromedriver service, and driver.start_session(capabilities) for reviving the active browser session with the given capabilities. (SeleniumBase UC Mode methods automatically use those raw selenium methods as needed.)
Links to those raw Selenium method definitions have been provided for reference (but you don't need to call those methods directly):
Also note that chromedriver isn't detectable in a browser tab if it never touches that tab. Here's a JS command that lets you open a URL in a new tab (from your current tab):
window.open("URL");--> (Info: W3Schools)
The above JS method is used within SeleniumBase UC Mode methods for opening URLs in a stealthy way. Since some websites try to detect if your browser is a bot on the initial page load, this allows you to bypass detection in those situations. After a few seconds (customizable), UC Mode tells chromedriver to connect to that tab so that automated commands can now be issued. At that point, chromedriver could be detected if websites are looking for it (but generally websites only look for it during specific events, such as page loads, form submissions, and button clicks).
Avoiding detection while clicking is easy if you schedule your clicks to happen at a future point when the chromedriver service has been stopped. Here's a JS command that lets you schedule events (such as clicks) to happen in the future:
window.setTimeout(function() { SCRIPT }, MS); --> (Info: W3Schools)The above JS method is used within the SeleniumBase UC Mode method: sb.uc_click(selector) so that clicking can be done in a stealthy way. UC Mode schedules your click, disconnects chromedriver from Chrome, waits a little (customizable), and reconnects.
🏆 Choosing the right CAPTCHA service for your business / website:

As an ethical hacker / cybersecurity researcher who builds bots that bypass CAPTCHAs for sport, the CAPTCHA service that I personally recommend for keeping bots out is Google reCAPTCHA:
Since Google makes Chrome, Google's own reCAPTCHA service has access to more data than other CAPTCHA services, and can therefore use that data to make better decisions about whether or not web activity is coming from real humans or automated bots.
⚖️ Legal implications of web-scraping:
Based on the following article, https://nubela.co/blog/meta-lost-the-scraping-legal-battle-to-bright-data/, (which outlines a court case where social-networking company: Meta lost the legal battle to data-scraping company: Bright Data), it was determined that web scraping is 100% legal in the eyes of the courts as long as: 1. The scraping is only done with public data and not private data. 2. The scraping isn’t done while logged in on the site being scraped.
If the above criteria are met, then scrape away! (According to the article)
(Note: I'm not a lawyer, so I can't officially offer legal advice, but I can direct people to existing articles online where people can find their own answers.)

